

 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
GaAsMask™
GaAsMask
uses a dark-field, "strong"
phase-shift mask design to produce quality sub-wavelength images to make
discrete GaAs gates.
This patent-pending method uses phase-shifted, subresolution assist features to shape the aerial image of the discrete diffraction pattern to
- eliminate zero order light, improving
depth of focus, and
- place two non-zero orders of light at the edge of the lens pupil plane, reconstructing the desired feature using two-beam interference.
Since
there is no electric field at the center of the pupil, the image is called
"strong"” shifted. Previous “weak” shifter
technologies do not eliminate the zero order energy.
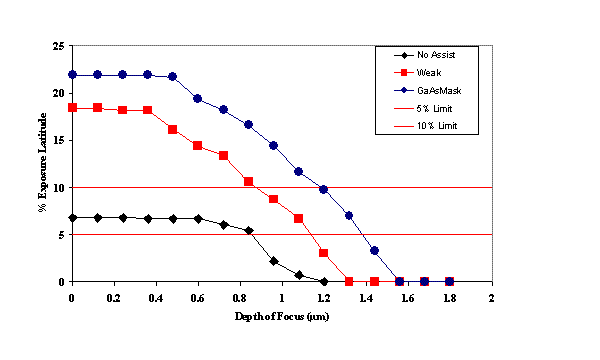
The
figure below compares simulated exposure latitude dependence on depth
of focus for a 240 nm isolated space imaged using a binary mask, a weak
phase shift mask, and new GaAsMask technology.* With no assist features,
the binary mask's depth of focus is 0.00 and 0.85 Ám, with exposure latitude
limits of 10% and 5%, respectively. At the same exposure latitude, the
weak shifted mask had focus latitudes of 0.88 and 1.15 Ám. The GaAsMask,
however, achieved 1.18 and 1.38 Ám focus latitudes.
* Simulations
made with PROLITH's lumped parameter model (FINLE Technology). Parameters
were: 0.5 NA, 365 nm wavelength, 0.3 sigma, contrast of 23, film thickness
of 700 nm, absorbance of 0.2 per micron, and diffusion length of 10 nm
GaAsMask™
is a collaborative project with 
Contact
us for more information about GaAsMask.
Semiconductor Links
Back to Products
|
© 2002 Petersen Advanced Lithography, Inc. |